Anti-inflammation
Our scientists have found, based on cell and animal studies, that N13-9-1 acts as an anti-inflammatory at the most critical level: it inhibits the excessive recruitment of white blood cells to sites of inflammation and so prevents tissue damage associated with immune cell build up.
Anti-inflammation
The anti-inflammatory effect of N13-9-1 is systemic and has the potential to prevent tissue damage in any organ of the body when the immune system is overactivated. The inflammation may be induced by any pathogen (bacterial or viral infection) or by metabolic disruptions. For example, experiments described in the patent show that N13-9-1 protects pancreatic tissue from damage caused by pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas). Most important, N13-9-1 normalizes the number of white blood cells at sites of inflammation, but it does not abolish the immune response by clearing all white blood cells.
Pancreatitis
The anti-inflammation activity of N13-9-1 was first tested in an established model for alcohol-induced pancreatitis. Animals were fed a regular diet including alcohol; the protocol includes some additional binge drinking to mimic a common pattern of human alcohol consumption. The continued alcohol intake causes an inflammatory response in the pancreas which involves the infiltration of neutrophils resulting in tissue damage, which is clearly seen as edema.
N13-9-1 has a dramatic effect when administered to the animals on alcohol: the pancreatic tissue is completely protected from tissue damage and appears normal; N13-9-1 also reduces the infiltration of neutrophils to normal levels so the trigger for tissue damage is removed.
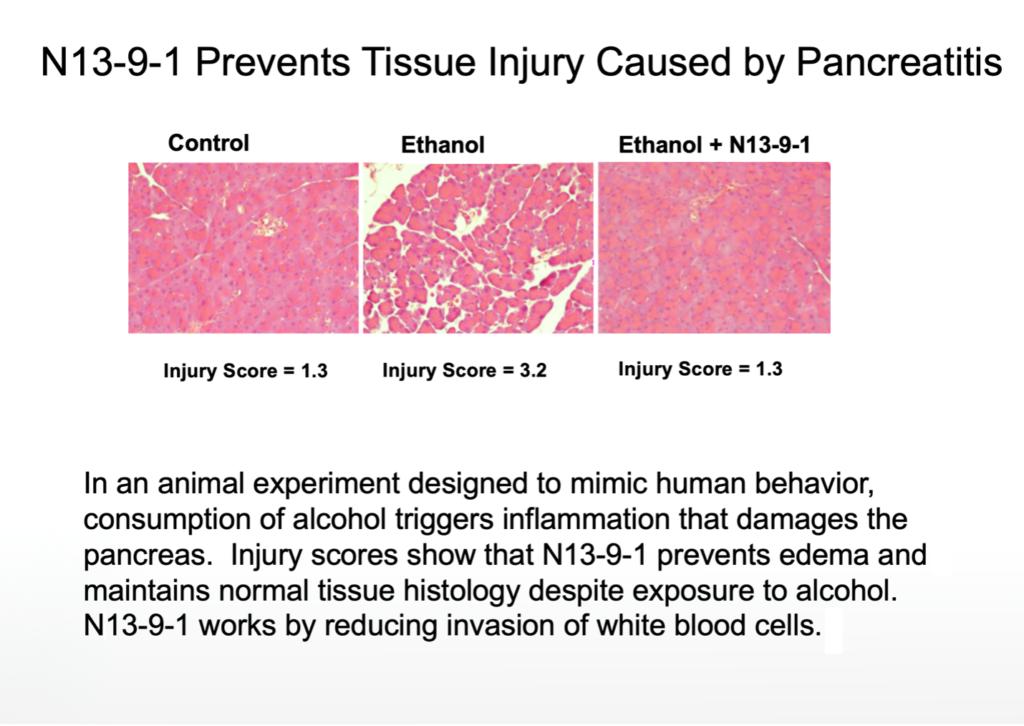
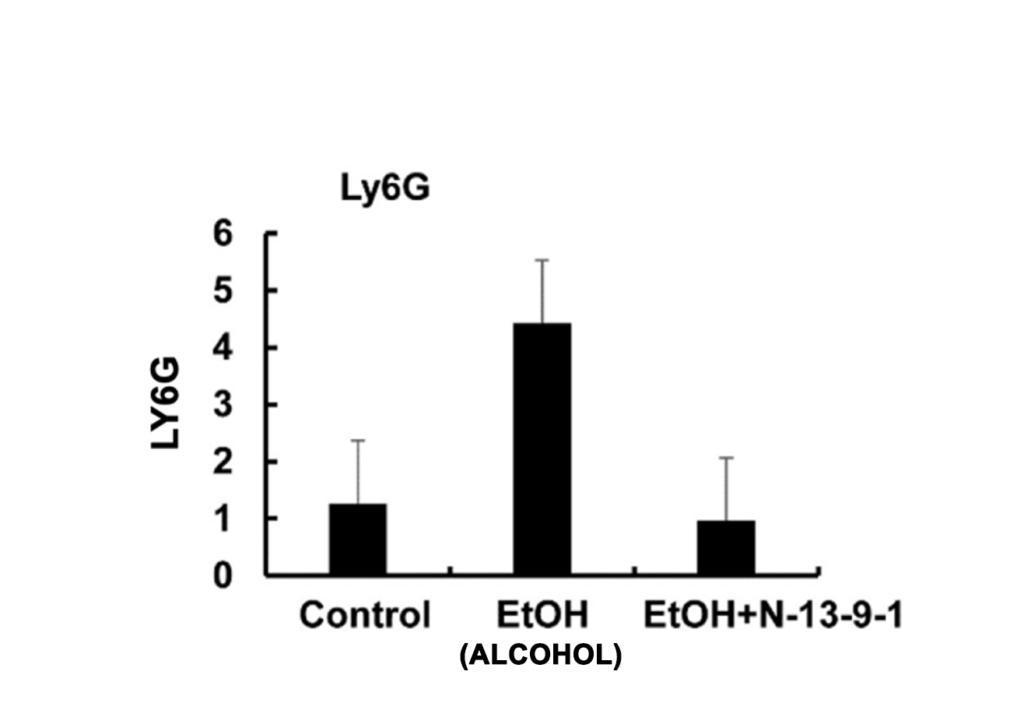
N13-9-1 REDUCES THE INVASION OF NEUTROPHILS IN PANCREATITIS
LY6G is a marker for neutrophils. In the experiment, N13-9-1 returns neutrophils to normal level seen in the Control. Note that N13-9-1 does not abolish neutrophils in the tissue, but normalizes the level of neutrophils.
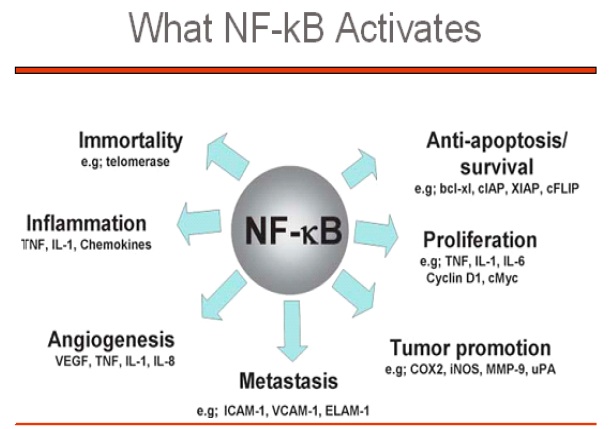
N13-9-1 suppresses activation of NF- ΚB in inflammation and cancer
One mechanism behind the anti-inflammatory activity of N13-9-1 is suppression of the transcriptional complex called NF- ΚB. Activation of this complex promotes a long list of chronic inflammations and suppression of this activation is a major goal of anti-inflammatory therapies. N13-9-1 is an effective suppressor of NF- ΚB activation. Activation of NF- ΚB also has profound effects in cancer by promoting survival, proliferation and metastasis of tumor cells. Suppression of NF- ΚB by N13-9-1 exerts multiple anti-cancer effects.
